
She holds a master's degree in finance and entrepreneurial management from the Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania. She is a business owner, interim CEO and author of "Solving the Capital Equation: Financing Solutions for Small Businesses." Wright has helped companies obtain more than $31 million in financing. Yahoo! Finance: Industry Browser - Grocery Stores - Company List.University of North Texas College of Business: Chapter 4: Analysis of Financial Statements - Answers to End-of-Chapter Questions.CDFI Fund: Understanding the Grocery Industry.McGraw-Hill Connect: Chapter 5: Income Measurement and Profitability Analysis - Part B: Profitability Analysis.Red flags are also triggered by unusually large changes.
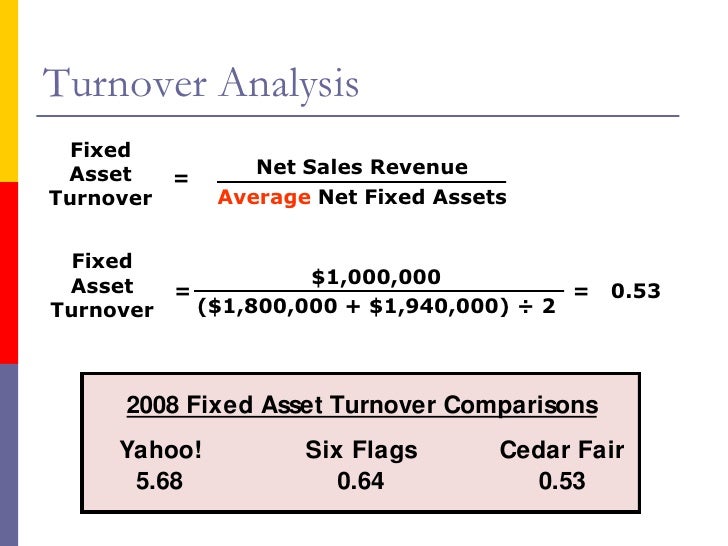
FIXED ASSET TURNOVER RATIO HIGH OR LOW HOW TO
How to calculate PPE turnover depends on all three of these assets. It calculates the net sales as a percentage of the company assets, indicating the sales generated from the company assets. it is too high or too low relative to peers). PPE turnover ratio, or fixed asset turnover, tells you how many dollars of sales your company receives for each dollar invested in property, plant, and equipment (PPE). An asset turnover ratio is a ratio that determines how efficiently a company uses its assets to generate sales. Our accounting screen is set to trigger a red flag when fixed assets/sales is below the 20th percentile or above the 80th percentile relative to industry peers (i.e. Small fixed assets can also mean small depreciation charges which flatters profits and may mean that the company has invested very little in tangible assets, despite growing sales or the need to replace worn out machinery. It may also suggest that the company does not own or cannot prove ownership of its fixed assets, hence, it does not book them on its balance sheet. A low level of fixed assets can indicate that a company is actually producing very little, its sales are fake, or it’s acting as an agent rather than the manufacturer it portrays itself to be. This might be acceptable in some industries, such as trading companies, but is unusual for the vast majority of industries. Fixed Asset Turnover Ratio Net Sales / (Fixed Assets Accumulated Depreciation) A high turnover ratio indicates the assets are being utilized efficiently for generating sales. Using the resulting ratio, the lender can compare the wood restoration professionals efficiency to other local businesses that have sought loans. A higher ratio is generally favorable, as it indicates an efficient use of assets. To calculate the ratio, you need to divide the net sales by the total property, plant, and equipment net of accumulated depreciation. Fixed asset turnover 150,000 / (75,000 - 25,000) 150,000 / 50,000 3.

Comparing the ratios of companies in different industries is not appropriate, as industries vary in capital intensiveness. The Fixed Asset Turnover Ratio measures the efficiency at which a company is capable of utilizing its long-term fixed asset base (PP&E) to generate revenue.

We are especially concerned about companies where net fixed asset turnover is extremely low relative to industry peers (i.e. Key Highlights The asset turnover ratio measures is an efficiency ratio that measures how profitably a company uses its assets to produce sales. For example, capital intensive industries (such as infrastructure) will have large fixed asset bases resulting in a high ratio in excess of 30x compared to asset light industries (such as IT) which will tend to have low ratios below 10x, as shown in Figure 23. Companies in the same industry should have a similar relationship between net fixed assets and sales although there will be huge differences across different industries. A low asset turnover figure would suggest either poor trading performance (which can be evaluated by the profit margin, sales per employee figures) or an over.
Net fixed asset turnover measures a company's ability to generate sales from its fixed assets. We also penalise any unusually large movements in either direction. We penalise companies that generate sales which are either unusually high or low relative to their net fixed asset base compared to industry peers.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
